

MVC is acronym for Model View Controller. It is an architectural pattern standard. Instead of writing all the php code and html markup in one file we segregate it. So say in a typical MVC framework there will be three folders:
Here is what each one of them will be doing
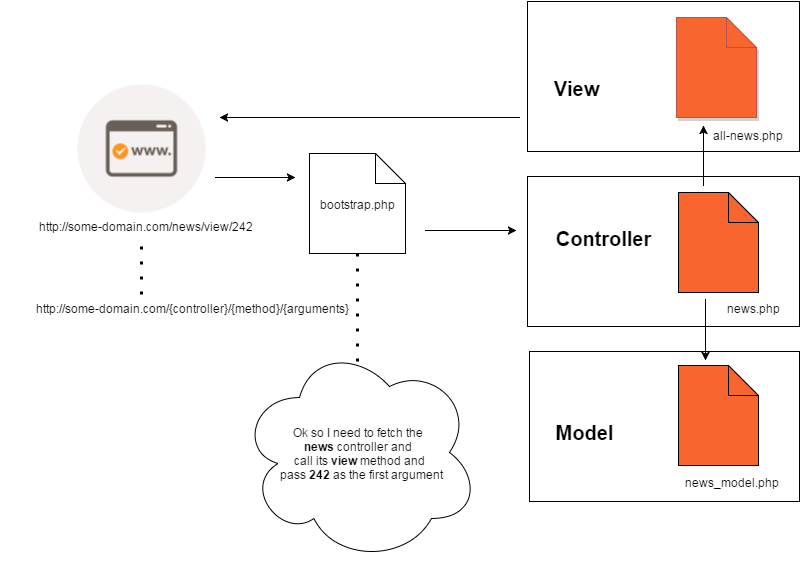
A framework that follows the conventional MVC pattern has a fix pattern of url structure. This is of the form http://some-domain.com/{controller}/{method}/{params}.
So say we have a webpage that displays all the news articles from database then the url would be something like http://some-domain.com/news/all. Here news will be our controller, which means there will be a news.php file containing a class News in the Controller directory. And this class will have a method all.
Similarly the url for a single news article page will be something like http://some-domain.com/news/view/212. So in the same class news there will be another method view which accepts one parameter.
So below is how our news class contoller will be looking like.
Now as said earlier the controller contains only the business logic. All the database queries are handled by the model. So say to fetch all the news from database we won’t be writing the database query in the Controller. But instead this will go in our model.
So in the Model directory there will be a file News_model.php
query("SELECT * FROM news ORDER BY publish_date");
return $all_news;
}
}
?>
And our controller will just call this method to fetch all the news.
get_all_news();
load_view('all-news',array('all_news'=>$all_news)); //this is equivalent to require_once('Views/all-news.php');
}
}
?>
The last line of the method uses load_view function. What this function will do is require_once the all-news.php file in the view folder and pass the $all_news variable to it. So this variable is available for use in the view file all-news.php.
Below is how our view file all-news.php would look like
content ?>
So as can be seen from above code, the html markup is inserted in view file. It’s upto the controller to decide which view file to use.
You must be eager to know how is it that automatically the controller class is called by the program. This is actually done using .htaccess and a bootstrap.php file.
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^ bootstrap.php [L]
What the above code does is redirect all the requests to bootstrap.php file. So even if you go to http://some-domain.com/anything, you will be redirected to bootstrap.php. However in the address bar you’ll see http://some-domain.com/anything although it will be the bootstrap.php file that you’ll be viewing.
$request_url = $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'];
$parts = explode('/', trim($request_url, '/'));
$controller = $parts[0];
$method = $parts[1];
$params = array_slice($parts,2); //remove first two elements aka controller & method
if( file_exists('Controller/'.$controller) ) {
require_once('Controller/'.$controller.'.php');
$controller_instance = new $controller;
if( method_exists($controller,$method) ) {
call_user_func( array( $controller_instance, $method ) );
}
else {
die("Controller method does not exist");
}
}
else {
die("Controller file does not exist");
}
Nowadays modern MVC framworks provide a routing class that specifies which controller to be called for a particular url. In contrast to the conventional url patter
http://some-domain.com/{controller}/{method}/{params} we can have a different controller to handle a particular request using the routing class. Below is how a typical routing class looks like:
get('news/all',array('News','all'));
?>
Above is a generic example. The actual class and method name and the way of calling the methods may differ from framework to framework. But the conceptual idea remains the same. Its the router that determines which controller class will handle which request.
In this tutorials we have tried explaining the concept using an example. Please note that we haven’t tried to create a MVC framework but instead understand how these frameworks work.
This is the best explanation of MVC that i ever got in web